Risk management and internal control system
STRUCTURE OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT SYSTEM AND INTERNAL CONTROL SYSTEM AT VOLKSWAGEN
The organizational design of the Volkswagen Group’s RMS/ ICS is based on the internationally recognized COSO framework for enterprise risk management (COSO: Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission). Structuring the RMS/ICS in accordance with the COSO framework for enterprise risk management ensures that potential risk areas are covered in full. Uniform Group principles are used as the basis for managing risks in a standardized manner. Opportunities are not recorded.
Another key element of the RMS/ICS at Volkswagen is the Three Lines Model, a basic element required by, among other bodies, the European Confederation of Institutes of Internal Auditing (ECIIA). In line with this model, the Volkswagen Group’s RMS/ICS has three lines designed to protect the Company from significant risks occurring.
The minimum requirements for the RMS/ICS, including the Three Lines Model, are set out in guidelines for the entire Group.
The RMS/ICS was further developed in the past fiscal year. The IT risk management system called “Riskradar” was introduced at all brands and significant Group companies in 2020. In this way, we have increased process and data security and reduced our manual workload through automated workflows and end-to-end system support for the analysis of data. At the same time, risk awareness at the Company is further intensified, risk transparency is improved and risks can be analyzed with end-to-end system support. The ICS has been standardized for high-risk business processes at significant companies. We will continue to develop our RMS/ ICS in the future.
THE VOLKSWAGEN THREE LINES MODEL
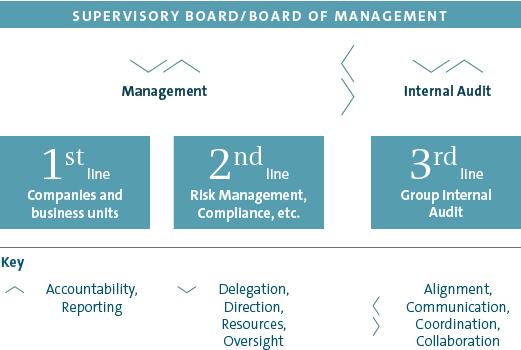
First line: Operational risk management
The first line comprises the operational risk management and internal control systems at the individual Group companies and business units. The RMS/ICS is an integral part of the Volkswagen Group’s structure and workflows. Events that may give rise to risk are identified and assessed locally in the divisions and at the investees. Countermeasures are introduced immediately, the remaining potential impact is assessed, and the information incorporated into the planning in a timely manner. Material risks are reported to the relevant committees on an ad hoc basis. The results of the operational risk management process are incorporated into budget planning and financial control on an ongoing basis. The targets agreed in the budget planning rounds are continually reviewed in revolving planning updates. At the same time, the results of risk mitigation measures are promptly incorporated into the monthly forecasts regarding further business development. This means that the Board of Management also has access to an overall picture of the current risk situation via the documented reporting channels during the year.
The operational risk management and internal control system also includes compliance with the so called Golden Rules in the areas of control unit software development, emission classification and escalation management. These rules are the minimum requirements in the organization, processes and tools & systems categories.
Second line: Identifying and reporting systemic and acute risks using Group-wide processes
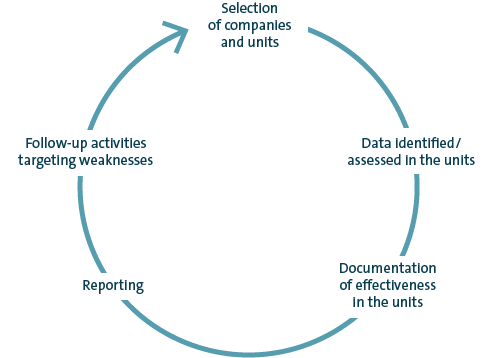
In addition to the ongoing operational risk management, the Group Risk Management department sends standardized surveys regarding the risk situation and the effectiveness of the RMS/ICS to the significant Group companies and units worldwide (regular Governance, Risk & Compliance (GRC) process) each year.
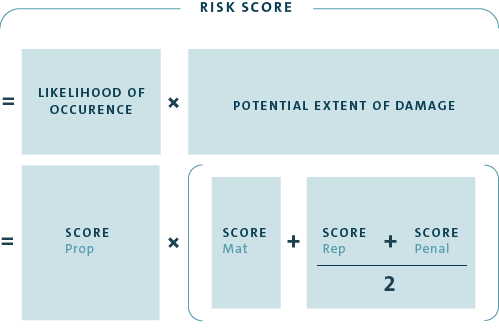
As part of this process, each systemic risk inherent to the process or inherent to the business that is reported is recorded and assessed in our RICORS IT system. The risk assessment is made by multiplying the criterion of likelihood of occurrence (Prob) by the potential extent of the damage. The extent of the damage is calculated from the criteria of financial loss (Mat) and reputational damage (Rep) and criminal relevance (Penal). A score between 0 and 10 is assigned to each of these criteria. The measures taken to manage and control risk are taken into account in the risk assessment (net perspective). The result is a risk score that expresses the risk.
The score for a likelihood of occurrence of more than 50% in the analysis period is classified as high; for a medium classification, the likelihood of occurrence is at least 25%. For the criterion of financial loss, the score rises in line with the loss; the highest score of 10 is reached when the potential loss is upwards of €1 billion. The criterion of reputational damage can have characteristics ranging from local erosion of confidence and loss of trust at local level to loss of reputation at regional or international level. Criminal relevance is classified based on the influence on the local company, the brand or the Group.
In addition to strategic, operational and reporting risks, risks arising from potential compliance violations are also integrated into this process. Moreover, the effectiveness of key risk management and control measures is tested and any weaknesses identified in the process are reported and rectified.
All Group companies and units selected from among the entities in the consolidated Group on the basis of materiality and risk criteria were subject to the regular GRC process in fiscal year 2020.
Quarterly risk reports are produced in addition to the annual risk assessment. These depict the Volkswagen Group’s acute – short to medium-term – risk situation. The assessment of risks from this quarterly risk process (QRP) is conducted in the “Riskradar” IT system similarly to that of the annual regular GRC process. All Group brands as well as Porsche Holding Salzburg, Volkswagen Financial Services AG and Volkswagen Bank GmbH are included in the QRP.
In addition, significant changes to the risk situation that can arise in the short term, for instance from unexpected external events, are reported to the Board of Management as required. This is necessary if, among other things, the risk may lead to potential financial loss of over €1 billion.
Based on the feedback from the annual regular GRC process and quarterly risk surveys, the overall picture of the potential risk situation is updated and the system’s effectiveness assessed.
A separate Group Board of Management Committee for Risk Management examines the key aspects of the RMS/ICS every quarter. Its tasks are as follows:
- to further increase transparency in relation to significant risks to the Group and their management,
- to explain specific issues where these constitute a significant risk to the Group,
- to make recommendations on the further development of the RMS/ICS,
- to support the open approach to dealing with risks and promote an open risk culture.
Risk reporting to the committees of Volkswagen AG depends on materiality thresholds. Systemic risks from a risk score of 20 and acute risks from a risk score of 40 or potential financial loss of €1 billion or more are regularly presented to the Board of Management and the Audit Committee of the Supervisory Board of Volkswagen AG.
CALCULATION OF RISK SCORE
Third line: Review by Group Internal Audit
Group Internal Audit helps the Board of Management to monitor the various divisions and corporate units within the Group. It regularly checks the risk early warning system and the structure and implementation of the RMS/ICS and the compliance management system (CMS) as part of its independent audit procedures.
ANNUAL STANDARD GOVERNANCE, RISK AND COMPLIANCE PROCESS
RISK EARLY WARNING SYSTEM IN LINE WITH THE KONTRAG
The Company’s risk situation is ascertained, assessed and documented in accordance with the requirements of the Gesetz zur Kontrolle und Transparenz im Unternehmensbereich (KonTraG – German Act on Control and Transparency in Business). The requirements for a risk early warning system are met by means of the RMS/ICS elements described above (first and second line). Independently of this, the external auditors check both the processes and procedures implemented in this respect and the adequacy of the documentation on an annual basis. The plausibility and adequacy of the risk reports are examined via spot checks in detailed interviews with the divisions and companies concerned together with the external auditors. The auditor examines the risk early warning system integrated in the risk management system with respect to its fundamental suitability of being able to identify risks that might jeopardize the continued existence and assesses the functionality of the risk early warning and monitoring systems in accordance with section 317(4) of the HGB.
In addition, scheduled examinations as part of the audit of the annual financial statements are conducted at companies in the Financial Services Division. As a credit institution, Volkswagen Bank GmbH, including its subsidiaries, is subject to supervision by the European Central Bank, while Volkswagen Leasing GmbH as a financial services institution and Volkswagen Versicherung AG as an insurance company are subject to supervision by the relevant division of the Bundesanstalt für Finanzdienstleistungsaufsicht (BaFin – the German Federal Financial Supervisory Authority). As part of the scheduled supervisory process and unscheduled audits, the competent supervisory authority assesses whether the requirements, strategies, processes and mechanisms ensure solid risk management and solid risk cover. Furthermore, the Prüfungsverband deutscher Banken (Auditing Association of German Banks) audits Volkswagen Bank GmbH from time to time.
Volkswagen Financial Services AG operates a risk early warning and management system. Its aim is to ensure that the locally applicable regulatory requirements are adhered to and at the same time to enable appropriate and effective risk management at Group level. Important components of it are regularly reviewed as part of the audit of the annual financial statements.
Monitoring the effectiveness of the risk management system and the internal control system
To ensure the effectiveness of the RMS/ICS, we regularly optimize it as part of our continuous monitoring and improvement processes. In the process, we give equal consideration to both internal and external requirements. External experts assist in the continuous enhancement of our RMS/ICS on a case-by-case basis. The results culminate in both regular and event-driven reporting to the Board of Management and Supervisory Board of Volkswagen AG.
THE RISK MANAGEMENT AND INTEGRATED INTERNAL CONTROL SYSTEM IN THE CONTEXT OF THE FINANCIAL REPORTING PROCESS
The accounting-related part of the RMS/ICS that is relevant for the financial statements of Volkswagen AG and the Volkswagen Group as well as its subsidiaries comprises measures intended to ensure that the information required for the preparation of the financial statements of Volkswagen AG, the consolidated financial statements and the combined management report of the Volkswagen Group and Volkswagen AG is complete, accurate and transmitted in a timely manner. These measures are designed to minimize the risk of material misstatement in the accounts and in external reporting.
Main features of the risk management and integrated internal control system in the context of the financial reporting process
The Volkswagen Group’s accounting is essentially organized along decentralized lines. For the most part, accounting duties are performed by the consolidated companies themselves or entrusted to the Group’s shared service centers. In principle, the audited financial statements of Volkswagen AG and its subsidiaries prepared in accordance with IFRSs and the Volkswagen IFRS Accounting Manual are transmitted to the Group in encrypted form. A standard market product is used for encryption.
The Volkswagen IFRS Accounting Manual, which has been prepared in line with external expert opinions in certain cases, is intended to ensure the application and assessment of uniform accounting policies based on the requirements applicable to the parent. In particular, it includes more detailed guidance on the application of legal requirements and industry-specific issues. Components of the reporting packages that are required to be prepared by the Group companies are also set out in detail there, and requirements have been established for the presentation and settlement of intragroup transactions and the balance reconciliation process that is based on these.
Control activities at Group level include analyzing and, if necessary, adjusting the data reported in the financial statements presented by the subsidiaries, taking into account the reports submitted by the auditors and the outcome of the meetings on the financial statements with representatives of the individual companies. These discussions address both the plausibility of the single-entity financial statements and specific significant issues at the subsidiaries. Alongside plausibility checks, other control mechanisms applied during the preparation of the single-entity and consolidated financial statements of Volkswagen AG include the clear delineation of areas of responsibility and the application of the “four eyes” principle.
The combined management report of the Volkswagen Group and Volkswagen AG is prepared – in accordance with the applicable requirements and regulations – centrally but with the involvement of and in consultation with the Group units and companies.
In addition, the accounting-related internal control system is independently reviewed by Group Internal Audit in Germany and abroad.
Integrated consolidation and planning system
The Volkswagen consolidation and corporate management system (VoKUs) enables the Volkswagen Group to consolidate and analyze both Financial Reporting’s backward-looking data and Controlling’s budget data. VoKUs offers centralized master data management, uniform reporting, an authorization concept and the required flexibility with regard to changes to the legal environment, providing a future-proof technical platform that benefits Group Financial Reporting and Group Controlling in equal measure. To verify data consistency, VoKUs has a multi-level validation system that primarily checks content plausibility between the balance sheet, the income statement and the notes.